Monday, 15 August 2022
Sātārā - The city which gets its name from the seven forts (Sat-Tara)
AMRAVATI - City of immense cultural and religious importance in Maharashtra.
The star city bus services are run by the Amravati Municipal Corporation. Private auto rickshaws and cycle rickshaws are also popular. Amravati has also started a Women's Special City bus which is a first in the Vidarbha region.
The Maharashtra State Road Transport Corporation (MSRTC) provides transport services for intercity and interstate travel. Many private operators also ply on the highly traveled Amravati – Pune and Amravati – Indore route. Bus services to cities like Nagpur, Yavatmal, Bhopal, Harda, Indore, Raipur, Jabalpur, Mumbai, Pune, Akola, Dharni, Nanded, Aurangabad, Jalna, Burhanpur, Parbhani, Solapur, Khandwa, Gondia, Shirdi, Hyderabad, Paratwada (Achalpur) and Kolhapur are also available.
National Highway 6 (old numbering), which runs from Hazira (Surat) to Kolkata, passes through Amravati.
New Star City Buses are launched in the city replacing the old city buses.
Railway
Amravati has three railway stations:Amravati railway station, situated in the heart of the city is a terminus. The railway line could not be extended beyond it. Therefore, a new station was constructed outside the city when a new railway line was laid to connect Badnera junction to Narkhed on the Nagpur-Itarsi main railway line. Amravati railway station is situated on the branch line from Badnera on Nagpur-Bhusawal section of Howrah-Nagpur-Mumbai line of Central Railways.
New Amravati railway station building was inaugurated on 10 December 2011. Amravati railway station provides multiple shuttle services to Badnera throughout the day.
Badnera Junction railway station serves the area of Badnera in Amravati. It is a junction station on the Howrah-Nagpur-Mumbai line. There is a broad gauge line to Narkhed.
Amravati Railway StationAirport
Dr. Panjabrao Deshmukh Airport Amravati, located at Bellora, 15 kilometers from NH-6 towards Yavatmal, is operated by the Maharashtra Airport Development Company (MADC). Presently it has no commercial scheduled flights. The Nagpur Flying Club has applied to DGCA for permission to shift its flying operations to Amravati airport.[13] It also has a helipad facility. MADC is acquiring about 400 Hectares of land for developing the airport and related facilities at an estimated cost of Rs. 2.25 billion.[14]
Development implementation in Amravati
Sunday, 14 August 2022
THANE- WITNESS THE RISE OF THE CITY OF LAKES
Thane (Marathi: [ˈʈʰaːɳeː]; also known as Thana, the official name until 1996) is a metropolitan city in Maharashtra, India. It is situated in the north-eastern portion of the Salsette Island. Thane city is entirely within Thane taluka, one of the seven talukas of Thane district; also, it is the headquarters of the namesake district. With a population of 1,841,488 distributed over a land area of about 147 square kilometres (57 sq mi), Thane city is the 15th most populated city in India with a population of 1,890,000 according to the 2011 census.
Located on the northwestern side of the state of Maharashtra, the city is an immediate neighbour of Mumbai city and a part of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region
Etymology and other names
The word 'Thane' is derived from local Marathi word "ठाणे" meaning "Police Check Post". Thane was the next Major British Police Check Post after Mumbai (formerly Bombay).
The name Thane has been variously Romanised as Tana,[2] Thana,[3] Thâṇâ,[4] and Thame.[5] Ibn Battuta and Abulfeda knew it as Kukin Tana; Duarte Barbosa as Tana Mayambu.[6] Before 1996, the city was called 'Thana', the British spelling of the city, until it was replaced with the more-local name.
Transport
Railways
Thana was the terminus for the first ever passenger train in Asia. On 16 April 1853, the passenger train service was inaugurated between Bori Bunder (Bombay) and Thane.[9] Covering a distance of 34 km (21 mi), it was hauled by three locomotives: Sahib, Sindh and Sultan.
Thane is connected with neighbouring suburbs through Central and Trans-Harbour Line Suburban railway network. Thane is a railway junction for the Thane-Vashi & Panvel Harbour Line and Central Line. It is one of the busiest stations in India and handles 654,000 passengers daily.[10][11]
Metro
As of 2019, Wadala and Thane are being connected through a Metro line.[12]
On 26 August 2015, the MMRDA sanctioned ₹354 billion for 118 km Mumbai metro network. This includes a 40-km Wadala-Ghatkopar-Thane-Kasarvadavali Metro-4 corridor via Wadala GPO and R.A.Kidwai Marg costing ₹120 billion.[13]
As of January 2021, the MMRDA, the nodal agency for building 300 km of vast Metro network, has proposed a plan to build an elevated depot for three Metro lines : 4 (Wadala-Thane-Kasarvadavali), 4A (Kasarvadavali-Gaimukh), 10 (Gaimukh-Shivaji Nagar) and 11 (Wadala-General Post Office, CSMT) at one stop. This depot is proposed at Mogharpada, Thane. The total project cost is estimated to be ₹ 596.60 crore.[14]
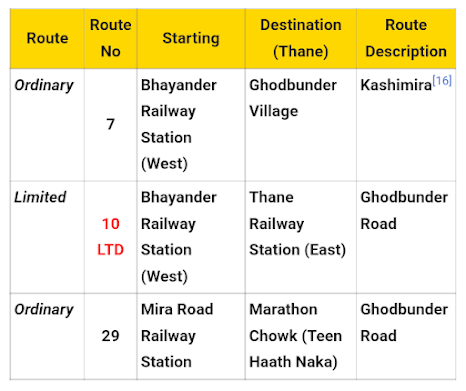
Thane Municipal Transport (TMT)
Thane Municipal Corporation started its own transport service on 9 February 1989, known as Thane Municipal Transport (TMT). TMT provides services the city interior and Mumbai suburbs like Mulund, Andheri, Mira road, Nala Sopara, Bhiwandi, Vasai, Virar, Borivali, Vashi, Airoli, Ghatkopar, Dadar, Bandra, BKC, Bhayandar, Kalyan, and Panvel, among others.[15]
Area• Total - 147 km2 (57 sq mi)• Rank - 15
Population (2011)• Total - 1,886,941• Rank - 15• Density- 13,000/km2 (33,000/sq mi)Demonym(s) - ThanekarLanguage• Official - Marathi
Time zone - UTC+5:30 (IST)
PIN - 400601—15Telephone code - 022Vehicle registration - MH-04 (Thane City) MH-05 (Kalyan)Lok Sabha constituencies - Thane,KalyanVidhan Sabha constituencies - ThaneKopri-PachpakhadiOvala-MajiwadaMumbra-KalwaLiteracy (2017-18) - 91.36%Website - thanecity.gov.in
Sātārā - The city which gets its name from the seven forts (Sat-Tara)
Satara (ISO: Sātārā) is a city located in the Satara District of Maharashtra state of India, near the confluence of the river Krishna and it...

-
Amravati is the second largest city in the Vidarbha region and ninth largest city in Maharashtra, India. It is administrative headquarter of...
-
Thane (Marathi: [ˈʈʰaːɳeː]; also known as Thana, the official name until 1996) is a metropolitan city in Maharashtra, India. It is situated ...
-
Navi Mumbai (Marathi pronunciation: [nəʋiː mumbəiː] , is a planned city situated on the west coast of the Indian subcontinent, lies in Kon...